| Terms |
Definition |
| Action |
These are tasks to be performed to notify the user, when alarms are generated by Applications Manager.For example, while monitoring WebLogic server, if the user wants to be intimated when the server response time is greater than 1000ms, then an alarm is generated when the condition is met. The users are notified of the alarms through Actions such as sending e-mail, SMS, trap, and executing a command. |
| Admin Activities |
Activities allowing IT administrators to configure any operation in Applications Manager with ease. Only the 'Admin' user can perform these activities. For more information on user access, refer to the User Administration section. |
| Alarms |
Alarms are notifications generated based on Threshold / Health values .They are generated when the value of a numerical attribute exceeds the pre-defined threshold limit. Additionally, the status of health and availability of an application can also be determined through Alarms. |
| Alarm Configuration |
This activity enables the user to associate a threshold profile with an attribute so that alarms are generated. It includes associating the action to be executed when an alarm is generated.Additionally, the dependencies for the ‘Health’ attribute of a Monitor can also be configured. |
| Attribute |
Attributes are parameters/objects of a Monitor and they provide information about them. These are parameters whose values are set to threshold to generate alarms. |
| Availability |
An attribute that determines whether a system or application is available for use (Up or Down). For example, if a Web server is running, then the availability is up.Consider a situation where the Web server may be running fine but its response time is high. This is indicated by Availability as Up  and Health as critical and Health as critical  if the response time is a dependent parameter for health. if the response time is a dependent parameter for health. |
| Monitor Groups |
Refers to the logical grouping of one or more Monitors such as application servers, network services, databases, web applications etc. This provides a holistic view of the business environment. |
| Custom Monitor |
Custom Monitors provide a way to monitor your Java applications or other applications that expose management information through SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and JMX (Java Management Extensions).Say, you have a Java application with built-in manageability using JMX and any application that has an SNMP interface, then they are managed by building Custom Monitors. |
| Dependencies |
Dependencies determine
- health of Monitor or Monitor Group
- health or availability of Monitor Group
They consist of the dependent parameters of the Monitor based on which the severity of the health and availability is determined. For example, Health of a Tomcat Server may depend on the overall response time of the server or on the response time of each of the web applications deployed on the server etc. By configuring dependencies, you can determine the attribute, based on which the severity of health changes. |
| Discover Network |
Locating all Monitors running within a network range. |
| Enterprise OID in SNMP Trap |
OID that uniquely distinguishes traps of different organizations, i.e. they vary for different vendors. This field applies only to SNMPv1 traps. |
| Generic Type in SNMP Trap |
These are types that are mapped to specific OID to generate SNMP traps and provide additional information about the functioning of the Monitor Group. They are applicable only to SNMPv1 traps. The different types of Generic traps are coldStart, warmStart, linkDown, linkUp, authenticationFailure, and egpNeighborLoss. |
| Health |
An attribute that indicates the quality of Monitors, based on their dependencies. For example, If a Web server takes 10 mins to respond, its response time is high but the server is still available. Hence it is indicated by Health as critical (If response time is a dependent parameter of health) and Availability as up (If response time is a dependent parameter of health) and Availability as up  . . |
| Monitoring |
It is a continuous process that uses methodical collection and analysis of data to provide business management. |
| Monitor |
Application on which monitoring is performed. Monitor is an instance of a Monitor Type that is running in a port of a host. For example, Application Servers such as WebLogic servers or Tomcat servers etc, Database servers such as Oracle or MySQL servers are some of the Monitor Types while a WebLogic server running on a particular port of a host is a Monitor. |
| Monitor Type |
Refers to application such as WebLogic server, JBoss server, System server, URL Monitor, Oracle Database server, MySQL Database server, etc. that are monitored by Applications Manager.Different instances of these applications are Monitor. |
| Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) |
The average time to repair a device or a system back to acceptable operating conditions. The term can also means, the time spent to restore a machine to operating condition after failure.This must be as low as possible. MTTR thresholds can be set to trigger root cause. |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) |
The average time that a device or a system worked without failure. The term also stands for the length of time a user may reasonably expect a device or system to work before an incapacitating fault occurs.This must be as high as possible. MTBF thresholds can be set to trigger root cause. |
| Polling Interval |
The time interval to monitor the different parameters configured for a Monitor. |
| RCA |
Root Cause Analysis helps to point the actual cause of a problem. You can view the 'Root Cause Analysis' by clicking on the status icon of the attributes. For example, 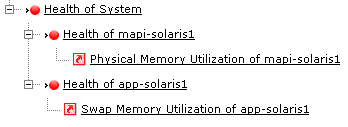 Expand the nodes to view the actual cause of the problem. Here, WebLogic Health is critical as Availability and Response Time (dependencies of Health) are also critical. Expand the nodes to view the actual cause of the problem. Here, WebLogic Health is critical as Availability and Response Time (dependencies of Health) are also critical. |
| Reports |
They provide organized presentation of data that depicts the behavior of Monitor Types over a specified period of time. |
| Response Time |
The time taken by a Monitor to react to a given input. |
| Severity |
Indicates how serious the problems are. There are three levels of severities: Critical, Warning, and Clear. These are controlled by the threshold set by the user or administrator. |
| SMTP Server |
An outgoing e-mail server using Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) that sends your outgoing messages to the appropriate recipients. Most e-mail systems that send mail over the Internet use SMTP to send messages. The messages can be retrieved using POP server. |
| SNMP OID |
Object identifier (OID) that is used to uniquely identify each object variable of a MIB (Management Information Base). |
| Specific Type in SNMP Trap |
When generic is set to Enterprise, a specific trap ID is identified. |
| SubNetMask |
The subnet mask determines the maximum number of hosts on a subnetwork. |
| Threshold |
Threshold is the value that determines the severity of the alarm based on the pre-defined conditions. For example, if the user wants to be intimated when the server response time is greater than 1000ms, then a threshold can be created based on this condition and assigned to the attribute. |
| URL Monitors |
Continuous URL monitoring service that monitors web pages. They verify the availability of specified, addressable, standard HTTP and HTTPS URLs of web pages. |
 Expand the nodes to view the actual cause of the problem. Here, WebLogic Health is critical as Availability and Response Time (dependencies of Health) are also critical.
Expand the nodes to view the actual cause of the problem. Here, WebLogic Health is critical as Availability and Response Time (dependencies of Health) are also critical.